|
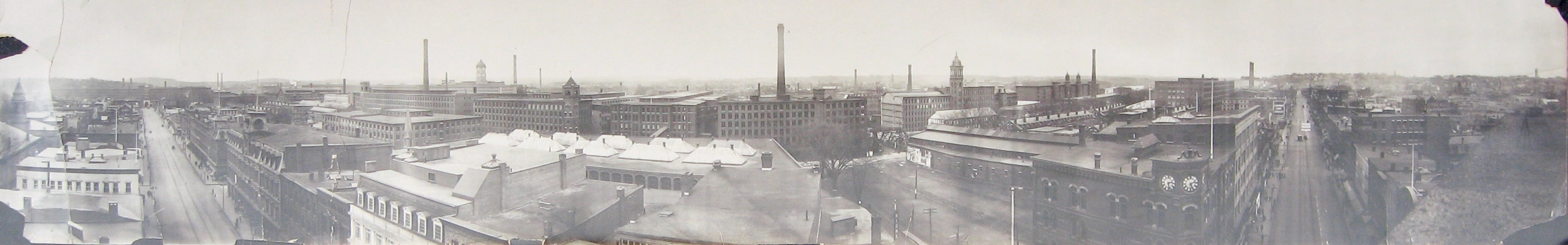
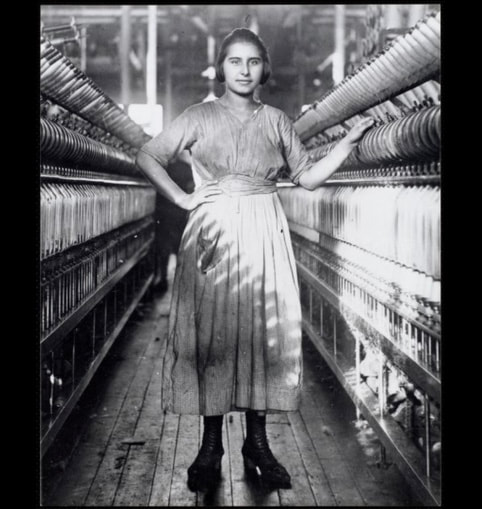
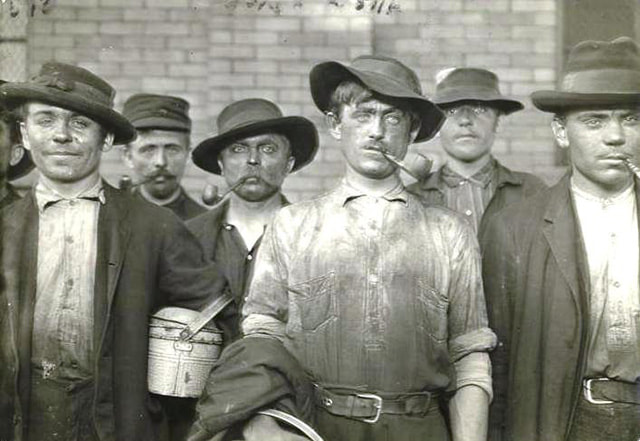
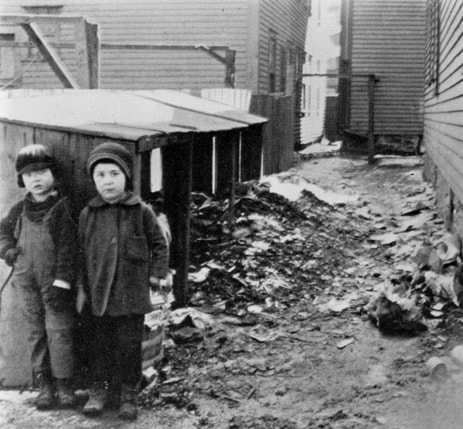
Above: Mill district panorama, circa 1910. Lawrence, Mass. (Source: Lawrence History Center) A LONG READ (sidebars about related topics are in blue font) In 1912, the city of Lawrence, Mass., population 85,000, was the worsted woolen capital of the world. Founded in 1845 as a planned industrial city, by the time of the strike, it employed 37,000 mill workers. Most were employed by the American Woolen Company, the country’s preeminent manufacturer of worsted woolen cloth. Over 7,000 workers toiled in the Wood Mill and Ayer Mill, that company’s main facilities. Other major mills of other manufacturing companies included the Washington Mill (5,000 employees) and the Arlington Mill (7,000 employees). Other mills also employed substantial numbers of workers. Not all hands were equal. Workers in skilled jobs – loom fixers and mechanics – were paid one rate, while “operatives” who tediously watched over automatic looms, were paid the lowest. A subsequent Congressional investigation into the strike said the average weekly pay for all workers was $8.76. For the most skilled workers, average pay was $11.39 a week. For Italians, the average was only $6.81, not enough to pay for food and rent in most cases. Whole families worked to make ends meet. (Source: Congressional Report on the Strike of Textile Workers in Lawrence, Massachusetts, 1912) Below: Mary Tomacchio, age 15, Ayer Mill (photo by Louis Hine). Louis Hine did portraits of over a dozen Italian immigrant children laborers in Lawrence. A decade earlier, there hardly were any Italians in Lawrence. In 1890, Lawrence had only 263 people born in Italy. Apparently, in 1891, around forty of them were brought in by people-smugglers known as padrone to work as strikebreakers (source: Immigrant City by Donald Cole). Sidebar about the padrone labor system: "Approximately 35 million immigrants entered the United States between 1820 and 1924, including 4 million Italians. They came largely from southern Italy, where an increasing population strained already meager resources. It became common practice for construction managers in Massachusetts and other states to hire labor agents (or padroni) to provide labor gangs for projects such as digging, laying railroad tracks, and supplying builders with materials. The padrone received a fee for each laborer he provided, and the laborer was provided with a steady income and a place to live in exchange for his labor. The padrone would provide housing, food, medical care, transportation, and, at times, liquor, charging most of the laborer’s wages. In many cases, the accommodations provided by the padrone were inadequate and sometimes nonexistent. After spending several months in backbreaking, dangerous work, the laborer would often be in debt to the padrone. These conditions led to sudden strikes, causing disruptions in various commercial construction ventures. For example, in the 1893, on the construction of the Wachusett Water project near Clinton, Italian laborers struck six times during the first four years of work. By 1900, there were approximately three thousand Italian laborers in Boston and some seven thousand in Massachusetts. Over the next few years, thousands more arrived in the Commonwealth in search of work. In 1904, a few Italian workers joined the building trades unions, but the vast majority of Italians on job sites remained unorganized and in bondage to the padroni. The Italian consul in Boston, Baron Gustavo Tosti, believed the only way that Italian laborers could erase the stigma of “cheap labor” that attached to them would be to organize their own union. An immigrant banker from Boston’s North End named Domenic D’Alessandro became a close ally of Tosti. D’Alessandro used his organizing talents to create the Italian Laborers Union (ILU) in April 1904, which became a key weapon in the attack on the padroni system. With the help of the Italian consul and the American Federation of Labor, the ILU in Massachusetts eventually encouraged the enactment of laws that put many padroni out of business and alleviated many injustices experienced by Italian immigrants." (Source: Commonwealth of Toil- History of Massachusetts Workers and their Unions, by Juravich et al 1996) Above: Italian Steelworkers circa 1910 by Lewis Hine. As the most recent immigrant group, Italians in the first years of the twentieth century often did the hardest, dirtiest jobs At that early time, most Italian workers were transient men who came to work and then intended to go back home again. In 1900, there were 963 Italian-born persons, still most of them men. But by 1915, there were almost 9,000 Italian born persons and their American-born children. “The exodus of southern Italians from their villages at the turn of the twentieth century has no parallel history,” said one writer. “Of total population of fourteen million in the South at the time of national unification 1860, least five million – more than third of the population – had left to seek work overseas by the outbreak of World War. The land literally hemorrhaged peasants.” (Source: From Italy to Boston's North End: Italian Immigration and Settlement, 1890-1910 by Stephen Puleo, master’s thesis, University of Massachusetts Boston.) Italian workers, as newcomers, were mostly likely to be overcrowded into overpriced tenements near the mills of Lawrence. Many lived with, or were, borders to make ends meet. The Italian immigrants were clustered around the eastern end of Common Street (if they were from Sicily) or Oak and Elm Streets (if they were Neapolitan). They had higher rates of mortality, despite a better diet, and high rates of child labor. In other similar nearby enclaves lived other recent immigrant groups, Lithuanians, Poles and Syrians. These groups comprised most of the rest of the lowest paid laborers in the mills besides the Italians…and the bulk of the non-Italian strikers. In contrast, the Irish, now established three generations, and French Canadians, one or two generations, were generally not big participants in the strike. 1911 photo of alleyway in Lawrence tenement district (source: White Fund) How did the strike come about? Thanks to progressive political activism by well-meaning socialites from Boston, the Massachusetts legislature mandated a reduction in the work-week from 56 hours to 54 hours, effective January 1, 1912. The mill owners resolved to reduce pay by two hours because of fewer hours worked. None of the Lawrence mill workers seemed to mind that they were dismissed twenty minutes earlier each day. However, when the first pay packets came on Friday, January 12, there was going to be hell to pay. Workers said they could not afford to lose the few pennies represented by those two hours. The Lawrence Sun of Thursday, January 11, 1912, carried the following news item with large head lines across two columns: ITALIAN MILL WORKERS VOTE TO GO OUT ON STRIKE FRIDAY. IN NOISY MEETING 900 MEN VOICE DISSATISFACTION OVER REDUCED PAY BECAUSE OF 54-HOUR LAW A mass meeting of almost all the Italian mill workers of this city was held Wednesday evening in Ford’s Hall. The object of the meeting was to discuss the new 54-hour law and to hear the reports of the different committees which had interviewed their respective mill agents. The reports were unfavorable to the 900 people who jammed the hall. It was decided that all Italians of all the mills strike on next Friday evening. They claim that the wages which they now receive because of the 54-hour law are not sufficient for them to live on, and that they want their pay raised to the amount which they formerly received. The meeting was presided over by Angeline Rocco. Who was this Angeline (or Angelo) Rocco? Rocco was a twenty-eight-year-old junior at Lawrence High School, a summer mill worker, and secretary of the Italian branch of Local 20 IWW, the International Workers of the World, which had only around 400 members in Lawrence. As I explained in my blog post about the 1919 Strike, the IWW was the union of the unskilled workers. It called for class warfare. Their charter read “The working class and the employing class have nothing in common. There can be no peace so long as hunger and want are found among millions of the working people and the few, who make up the employing class, have all the good things of life." You can see Angelo Rocco talking about the strike in this video taken in 1977: The Strike Here is how the 1912 strike went down. According to the Congressional strike report, “On the Friday morning succeeding the strike, at the Everett mill it was evident that the employees expected their pay envelopes to show reduced earnings and that they determined upon resistance to a reduction in earnings. In one of the large departments the non-English-speaking employees by 9 o’clock had begun to leave their work, to congregate in groups, and to show signs of excitement. Word to this effect reached the pay department and fearing an outbreak the distribution of the pay envelopes was delayed. A short time afterwards word came from the mill that rioting had begun in some departments and that employees were stopping machinery and driving other employees from their work. A call was sent to the mill office for police, and a small number of police responded. They failed to get the employees creating the disturbance out of the mill, and a call was sent in for more policemen. Shortly after the arrival of the second group, the strikers—a small number at a time—began to come out of the mill and congregate just outside the mill gates. Those taking part in this demonstration and who formed the crowd outside the mill gates were principally Italian workers. As the crowd at the gate was increased by accessions from those within the mill, some of the leaders began to make speeches, and after a short time the entire crowd, carrying an Italian flag and a large number of United States flags, started on a march toward the Wood mill of the American Woolen Co. The Wood mill is several squares below the Washington mill, and the striking Italians reached there in a short time, and rushed the gates and secured entrance to the mills, the gatekeepers and watchmen being unable to stop the inrush. The strikers then rushed into the different rooms of the Wood mill, shutting off the power from the machines and calling upon the workers of the Wood mill to join with them in the strike. After about one-half hour of disorder in the Wood mill the strikers withdrew, accompanied by a considerable number of the employees of the Wood mill in the departments which the strikers had been able to reach. In connection with the morning of disorder, the strikers in marching past one of the smaller mills destroyed a number of windows by throwing ice through them. Shortly afterwards a collision occurred between the strikers and the police, in which the police brought their clubs into use.” A committee, led by Angelo Rocco, was formed and they telegraphed the general executive board of the IWW in New York to send someone to lead the strike. On Saturday, January 13, Joseph (Giuseppe) Ettor of the IWW executive board arrived in Lawrence from New Jersey. Described by one critic as having "the cunning of the Syrian and the eloquence of the Italian," Ettor’s parents were from Italy and he spoke fluent Italian. Ettor was soon joined by Arturo Giovannitti, an Italian born poet and orator who was director of Il Proletario, a radical workers’ newspaper. Below: Italian-American strike leaders Ettor and Giovannitti arrive in Lawrence, January 13, 1912 SIDEBAR: Who were Ettor and Giovannitti? Here is a description of them from a book about Italian radicals in America in the early 20th century: “Only twenty-six years old, with a shock of curly black hair and a cherubic smile, Ettor looked more like a mischievous street urchin than a fiery labor agitator and the IWW’s principal organizer for its eastern branches. Born to Italian parents in Brooklyn, in 1886, Ettor grew up in Chicago and California and joined the SPA while still a teenager, working as an iron worker in a San Francisco shipyard. He joined the IWW in 1905 and served as an organizer among West Coast lumbermen, miners, railroad workers, and construction gangs. Elected to the IWW’s general executive council in 1908, Ettor moved East the following year. His proficiency with foreign languages (he was fluent in English and Italian, and understood Polish, Yiddish, and Hungarian) proved invaluable when dealing with immigrant workers such as those in Lawrence. The strike would prove to be the greatest triumph of his career in the labor movement. Ettor perceived at the outset that Italians mill workers, by virtue of their superior numbers and militancy, would constitute the backbone of the strike. To join him as co-leader of the Italians, Ettor invited Arturo Giovannitti, the director of Il Proletario, who arrived on January 20. At twenty-eight, Giovannitti was an elegant figure, taller and thinner than his stocky comrade, with handsome features and brooding eyes. Giovannitti had an unusual background for a sowersivo [“subversive”]. As a rebellious and melancholy youth from the middle class in Campobasso (Molise), Giovannitti rejected the prospect of life among the provincial bourgeoisie and migrated to Canada at age sixteen, supporting himself briefly as a mine worker and railroad laborer. Well educated but guided by religious and mystical tendencies, Giovannitti found work at a Presbyterian mission for Italians in Montreal, and studied English and theology at McGill University. He continued his religious studies at Columbia University’s Union Theological Seminary in 1904, while working at a Presbyterian mission in Brooklyn. After another stint at a mission in Pittsburgh, Giovannitti’s flirtation with Protestantism ended, and he embraced syndicalism under the influence of Carlo Tresca, with whom he maintained a lifelong friendship. Back in New York and unemployed, Giovannitti spent many a winter’s night sleeping on a bench in Little Italy’s Mulbury Park until he found work as a bookkeeper and joined the editorial staff of Il Proletario. Thereafter, his rise to prominence in the Italian syndicalist movement was rapid, becoming the director of the newspaper and FSI secretary in 1911. By that time, Giovannitti had also distinguished himself as the leading poet of the Italian immigrant Left, although much of his best poetry (in English) would soon be inspired by the ordeal that awaited him in Lawrence. Giovannitti’s role in the strike was that of the charismatic orator; his “Sermon on the Common” (in English), echoing Christ’s “Sermon on the Mount,” uplifted strikers’ spirits and strengthened their resolve to fight." (Source: Carlo Tresca, Portrait of a Rebel, by Nunzio Pernicone, AK Press 2010) The strike committee, made up of representatives of 43 different nationalities, put forward its demands on Sunday, January 14.
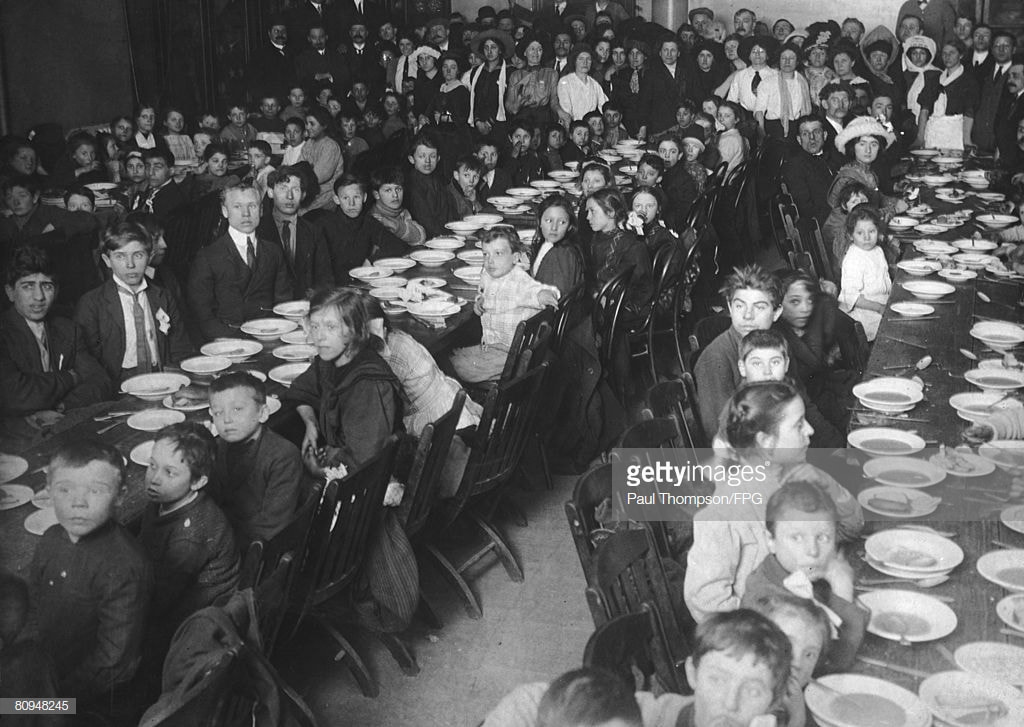
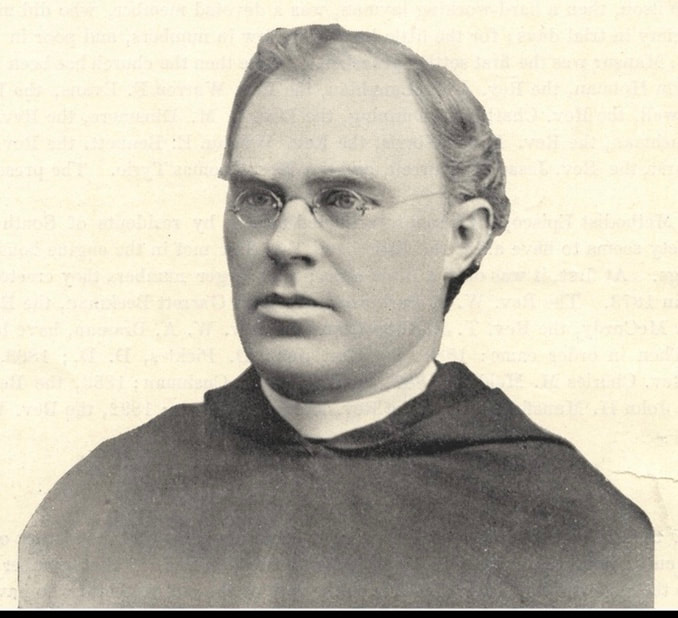
The demands of the strikers were ignored. The next day, 22,000 striking workers basically prevented non-striking workers from entering the mills, and 37 people were arrested in violent confrontations with police. This state of disruption continued for a couple weeks despite a furtive meeting between five members of the strike committee and representatives of Lawrence’s eight mill corporations. Below: Scene from the strike. Caption reads Pacific Mill watchmen turn hoses on strikers, January 15, 1912  For a few weeks, things looked like a stalemate, or war of attrition. Then there was a twist in the plot. During a clash between strikers and the police on Monday evening, January 29, Anna Lo Pizza, an Italian woman, was shot and killed. As a result of the disturbance of the day, the city council gave control of the city to the officer in command of the militia, Major Sweetser. Parading and assembling in the streets or on the common was ordered discontinued. The mayor also requested additional protection, and the governor ordered twelve companies of infantry, two troops of cavalry, and fifty police officers from the metropolitan police force to report at once in Lawrence. Below: Photo of one of the militia companies on duty in Lawrence during the 1912 strike In connection with the death of Anna Lo Pizza, the strike leaders Joseph J. Ettor and Arturo Giovannitti were arrested as accessories to the murder, along with the Italian worker charged directly with the murder, Joseph (Giuseppe) Caruso. Jailhouse photo of Caruso, Giovannitti and Ettor, charged with the murder of Italian striker Anna LoPizza On January 20, dynamite was found in three spots around the city, claimed to have been planted by anarchists among the strikers. Strike representatives claimed the dynamite had been planted by agents of the mills. Relief efforts were established. According to the congressional strike report, two soup kitchens were maintained by the Italians (on account of being the largest group presumably), one by the Syrians, one by the Polish, one by the Armenians, and one at the Franco-Belgian Hall for all nationalities not provided for elsewhere. “The strike relief committee investigated the cases of applicants for help to determine whether or not they were strikers, although the investigation was largely omitted in the case of the Italians, of which race practically everyone employed in the textile mills was on strike.” (emphasis added – it shows the overwhelming Italian participation in the strike.) Below: relief provided to children of strikers Despite the sidelining of Ettor and Giovannitti (who were later acquitted – see epilogue), the strike continued. By this time, the Catholic church leaders of Lawrence had gotten involved. The church in Lawrence was dominated by the Irish clergy who had built the Catholic Church in New England. There was also a large French-Canadian contingent, who had emigrated in the 1870s and 1880s. Among the Irish establishment, support was strong for the captains of order. Father Timothy J. Regan, an Irish priest at St Laurence O’Toole, served as chaplain for the militia (in part because most of the members of the militia were Irish). He would celebrate Sunday mass in the armory for the troops and their heavy-handed commander, Colonel E. Leroy Sweetser, who had led the attack on women and children when they were leaving the city on February 24. Regan praised the soldiers for “making it possible for every citizen willing and able to work to do so.” On the other hand, he did preach that owners had an obligation to ensure operators were paid adequately. This was the official posture of the Catholic church, set forth in the Rerum Novarum. (The Rerum Novarum was a papal edict from 1891 setting forth the proper relationship between labor – to work and obey – and capital – to provide.) In gratitude for his service, two military companies presented Father Regan with a "handsome and costly pair of gloves" and a shaving set. And at French-Canadian St. Anne’s, an unidentified priest told the press, "we have done everything to educate the people to obey the laws and customs of this country ... we knew nothing of the strike until it was upon us. Our congregation will go back to work." And Father Joseph W. Dreyer, a priest at the church, after reading portions of Rerum Novarum in his Sunday sermon, exhorted his parishioners to return to the mills. Contrast these pro-management responses of local Catholic priests with the response of the head priest of the Italian parish, Holy Rosary, named Mariano Milanese. His role in the history of Holy Rosary church is covered in another blog post. “The priest whose pro-strike comments and policies seemed to garner the most attention was Mariano Milanese. The Italian-born pastor of Holy Rosary parish had come to Lawrence in 1902 specifically to establish a church for Italians. Possibly more attention was paid to him than other priests because Italians, the largest immigrant group, were the backbone of the strike and provided local leadership. In addition, his church was located opposite the Everett Mill in the center of the turmoil. When Milanese was unsuccessful in persuading mill agents to raise wages, he read a letter to his congregation from William M. Wood, president of American Woolen, the city's largest mill. Although Wood asked the operators to return to work with the understanding he would increase wages when he could afford to do so, Milanese told his congregation their stand was correct. He would support them to the full extent of his powers and he then began to solicit funds for relief.” (James J. Kenneally, Catholic Clerical Quandary: The Lawrence Strike of 1912 in American Catholic Studies Vol. 117, No. 4 (Winter 2006)) Below: Father Mariano Milanese of Holy Rosary Church, the Italian congregation founded in 1904. Of the Catholic clergy, he was most sympathetic to the strikers, who were mostly Italian. By mid-February 1912, a more official Catholic response in Lawrence had been formulated by its Irish leadership. It was decidedly anti-strike. Father James O'Reilly, head of St. Mary’s and de facto head of all the Catholic churches in Lawrence, organized a public campaign against the dangers of socialism which nearly everyone equated with the IWW. On Sunday, February 25, pastors of three of the Irish churches criticized that doctrine. In a coordinated exercise, at different masses at St. Laurence, Regan asserted, "socialism, anarchy, agnosticism, and atheism are at our very door and must be fought". Meanwhile, Father McDonald at Immaculate Conception denounced socialism as the greatest enemy of the church and the world, and called upon Catholics to do their utmost against it. Then Father O'Reilly, at St. Mary’s, in a widely publicized sermon, asserted that the evils of socialism transcended the labor issues. Below: Father James O'Reilly, head priest of St. Mary's and head of the Augustinian order in Lawrence Despite these official church messages, however, Father Milanese continued his citywide appeal for strike funds, stating he was helping two hundred people a day. Father Milanese’s relief efforts, along with other church relief programs, had the effect of undermining reliance on IWW assistance. As Milanese observed, many parishioners were ashamed to go to the IWW strike committee for food and money; they certainly were not encouraged to do so by him. Other churches also held special collections and solicited contributions to the St. Vincent de Paul Society to assist strikers. Cardinal O'Connell contributed two hundred dollars to Milanese's fund. Yet Italians, often led by Rocco, had to go to the basement of St. Anthony's, the Syrian church, to meetings where they heard Ettor address them in their native language. He and any other Italian strike leaders were barred from Holy Rosary. Nevertheless, Rocco, never criticized Milanese. Milanese also often visited strike leaders Ettor and Giovannitti when they were jailed in the shooting death of Italian striker Anna LoPizza and supplied them with literature during the months they were incarcerated. Outcome of the 1912 Strike Upon the arrest of Ettor and Giovannitti, the IWW replaced them with Big Bill Haywood and other leaders, who worked with the multi-ethnic strike committee in Lawrence. As a result of the political backlash caused by reports of police attacking unarmed women and children, politicians in Massachusetts and Washington, D.C. began to clamor for some kind of settlement of the strike. Victory for the strikers was achieved on March 12, 1912, when all their demands were met. Below: Strikers voting to accept the strike terms, Lawrence Common, March 14, 1912 Epilogue - Continued IWW Struggle for Justice in Lawrence, Led by Italians for Italians Until Ettor and Giovannitti were set free, organizers had unfinished business. From April to October 1912, an unprecedented amount of activism occurred in Lawrence. Massive street marches, counter marches (the God and Country parade), violence, funerals. Much of this post-strike history seems to be forgotten in Greater Lawrence these days. Labor activist Carlo Tresca – who apparently did not speak English – was sent to Lawrence to address workers on May 1, so-called May Day, the international day of the worker. Tresca was a leader not only in the I.W.W. but also in the Federazione Socialista Italiana del Nord America (the FSI). His young Irish-American lover, Helen Gurley Flynn, had already been working in Lawrence for a number of months organizing workers. The activism was as much about Italian national pride as it was about worker solidarity. For this reason, the IWW were careful to choose an Italian organizer. “Although they never appealed to nationalist sentiments, FSI leaders understood that the agitation to liberate Ettor and Giovannitti was as much an ethnic conflict as a labor/political struggle. Leadership of the Italians therefore had to be entrusted to someone who commanded great respect among Italian workers, and who possessed exceptional talent as a strategist, agitator, and organizer. The man best qualified for the task, the FSI knew, was Tresca.” (Pernicone book on Tresca) “The Lawrence May Day parade attracted…5,000 members of the IWW, mostly Italians, including many women carrying infants and pushing baby carriages. A large rally was also held at the Essex County Jail on Hampshire Street, where the prisoners [Ettor and Giovannitti] were held, and later than evening Italian members of Local 20 conducted their own procession.” (Source: Pernicone) Below: Italian organizer and orator, Carlo Tresca. He arrived in Lawrence a month after the strike to try to maintain the revolutionary momentum of the strike to further organize the workers. He spoke no English, only Italian. The next mass protest was on Sunday, May 26, 1912, when the IWW conducted a funeral parade in honor of fallen workers Lo PIzzo and Ramey. Some 15,000 workers from Lawrence, Haverhill and other industrial towns participated. (Source: Pernicone) Photo: Demonstrators laying a wreath on the grave of fallen striker Anna LoPizza, Memorial Day 1912, more than two months after the strike ended To prevent further disturbance, the City prohibited demonstrations by the I.W.W. on public property. Tresca was not thwarted.
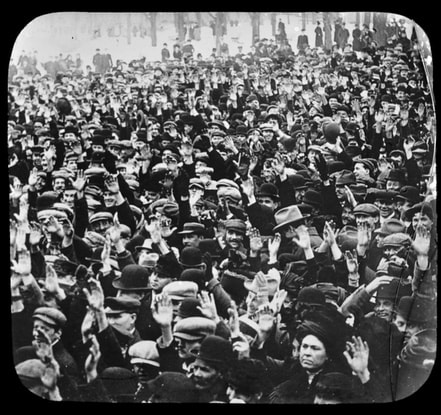
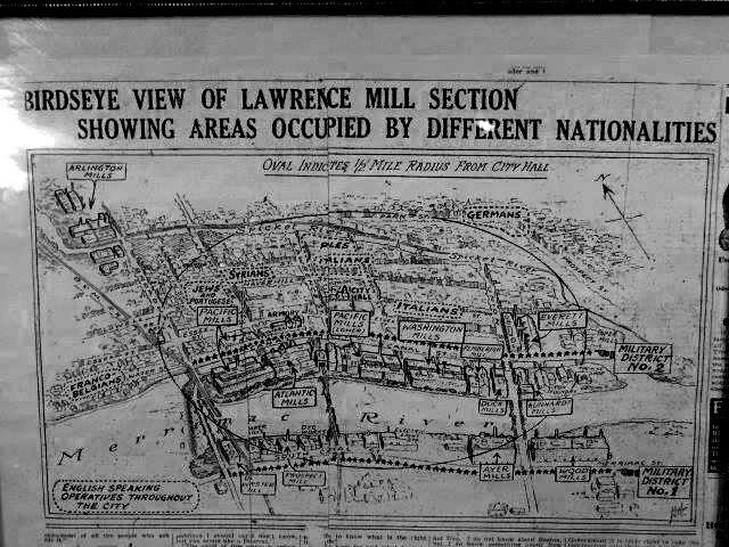
Tresca then approached prominent Italian-American banker Fabrizio Pitocchelli for money to support future demonstrations. “Reminding Pitocchelli that many of his Italian clients were IWW members, Tresca offered him a choice: provide money or face a boycott of his bank. A promise of money was immediately forthcoming.” (Source: Pernicone) On Sunday, September 24, a large rally of workers from Haverhill, Lynn, Lowell, New Bedford, Fall River and other industrial towns converged on Boston Common – 20,000 to 35,000 in all. (ibid). There, Bill Haywood called for a General Strike. However the next day, Ettor and Giovannitti sent letters urging workers not to engage in a general strike, because “the risk of failure was too great on the one hand and the temper of the workers, particularly the Italians, too explosive on the other.” In the meantime, the followers of Lynn-based anarchist, Luigi Galleani began to jockey to take control of the situation from Tosca. Rejecting even syndicalist unions as instruments of social struggle, Galleani placed his faith in all methods of revolutionary violence, including bombs and assassination. Thus, despite the call from Ettor and Giovannitti not to hold a general strike, on September 26, the anarchist leaders took up positions outside the mills and urged Italian workers to strike later that day. “By 3:15 p.m. on September 26, 1912, the Italians began streaming out of the mill, soon to be joined by Italians from the Washington Mill. At a large meeting at Lexington Hall that evening, the IWW and the Italian anarchists vied for leadership of the assembled crowd. Spurred by the exhortations of the anarchists, the Italian workers en masse voiced their desire for a general strike. The following morning, September 27, several thousand angry Italians abandoned the mills. Their belligerent mood quickly proved infectious, and some 10,000–12,000 workers went on strike the next day.” Below: Luigi Galleani, Italian anarchist and rival to the IWW, His followers also worked to agitate the Italian workers of Lawrence in the months after the strike SIDEBAR: Who were the Galleanists? They were a radical anarchist group that followed the teachings of Luigi Galleani, based in Lynn, Mass. Starting in 1917 when they came under increased government supression, they followed a path of violence. "It was in April of [1917] that the United States entered Word War I, to which Galleani and his followers were uncompromisingly opposed. This brought down upon them the full panoply of government repression. Throughout the country their Clubhouses were raided, men and women beaten, equipment smashed, libraries and files seized and destroyed. Their lectures and recitals were disrupted, and their newspapers and journals suppressed, among them Galleani’s Cronaca Sovversiva (the Subversive Chronicle), in which he denounced conscription and the war. The Galleanists viewed these developments with mounting indignation. Men of energy and determination, they could not stand idly by while their comrades were being imprisoned, their presses silenced, their meetings disrupted and dispersed. An overwhelming desire to retaliate, to strike back at the state that was stifling and crushing their movement, took possession of them. So it was that between 1917 and 1919, the height of the Red Scare, a group of anarchists came into being whose function was to carry out bombings. Sacco and Vanzetti were among them. They refused to turn the other cheek. Uncompromising militants, they rejected docile submission to the state. They were determined, on the contrary, to answer force with force, not only as a matter of self/defense but of principle and honor. The climax was reached in 1919, following a rash of anarchist deportations. Among those evicted from the country was Galleani himself. This proved the last straw. The Galleanists issued a leaflet threatening retaliation. “You have shown no pity to us,” it declared. “We will do likewise. And deport us! We will dynamite you! ” An enemies’ list was drawn up, to whom package bombs were sent in the mail. This occurred on the First of May, the premier working class and anarchist holiday. The list consisted of 30 names, including Attorney General A. Mitchell Palmer, Postmaster General Albert S. Burleson, Secretary of Labor William B. Wilson, Supreme Court Justice Oliver Wendell Holmes, Commissioner General of Immigration Anthony Caminetti, and US. District Judge Kenesaw Mountain Landis, as well as John D. Rockefeller, and P. Morgan, among others. Each of the intended victims had antagonized the Galleanists in some unforgivable way: arrested their comrades, closed down their newspapers, deported them to Italy, and the like. Additional bombs were delivered by hand to the doors of intended recipients. None of them was hurt, although the house! maid of one had her hands blown off and an elderly security guard was killed. To men of the bombers’ stamp, the use of violence was not a crime; it was a justifiable response to persecution. They considered themselves at war with the forces of government, and if they resorted to bombs it was as the government used bombs, for the purpose of war. Violence, in any event, was one of the few weapons at their disposal, a necessary means of self—defense. How else were they to retaliate against their tormentors?" Above: The Scandalous Protest Sign Declaring No God, No Master - Lawrence, Mass. Sept. 1912 To regain the upper hand against the followers of Galleani, the IWW organized another memorial parade on Sunday, September 29. That afternoon, “in defiance of the police and a torrential rain, 4,000 workers—most of them Italians—marched silently to the [St. Mary Immaculate] cemetery, with Tresca at the head, standing backward in a one-horse buggy. Tresca remembered that “one big banner, when all the others had given away to the force of the persistent downpour, remained intact. On it was a red, challenging motto, ‘No God, No Master.’ Above: Lawrence's Mayor, Michael A. Scanlon This message proved to be the last straw for business and church leaders in Lawrence. “Major Michael A. Scanlon called upon all the “patriotic and law abiding citizens” to wear American flag buttons in their lapels as a rebuke to the advocates of anarchy and atheism who had invaded their God-fearing city.” At a meeting in City Hall, Father James O’Reilly, the Catholic priest who was the most powerful man in Lawrence, shouted: “Those who do not want to work better take a hint and go. We will drive the demons of anarchism and socialism from our midst.” More than 100 private detective and thugs were hired, and were put to use during the 24-hour hour protest strike that took place on Monday, September 30 involving 10,000 workers. It became dangerous to wear an IWW pin. Below: An IWW pin of the kind that got Jonas Smolskas killed in October 1912 “To demonstrate that neither he nor the IWW could be intimidated, [Tresca] planned an act of defiance…on October 5. With his friend Bertrando Spada, one of the FSI’s foremost leaders, armed and walking behind to cover his back, Tresca strolled conspicuously up and down Essex Street wearing an IWW button in his lapel and secreting a revolver in his pocket, almost daring the detectives he encountered along the way to start trouble. None stepped forward to challenge the “Bull of Lawrence,” as he had come to be known.” However, on October 19, 1912 Lithuanian immigrant Jonas Smolskas was assaulted for wearing an IWW pin, and died three days later from his injuries. Below: Alleged photo of Jonas Smolksas. By the way, in this blog post, I'm not saying other ethnicities did not participate in the strike. The most noteworthy aspect of the strike was that over forty nationalities, the members of which spoke little English, coordinated their efforts so successfully. Rather, in this blog entry I point out that the strike was "Italian" insofar as (1) the significant majority of strikers were Italian immigrants, (2) and so were the majority of the strike leaders. I would suggest that one reason for this participation and leadership was the prevalence, at least at that time, of radicalism in the Italian immigrant community. Above: Map printed during strike showing locations of ethnic neighborhoods - Italians, Poles and Syrians concentrated in most densely populated area of tenement housing A few days before the death of Smokskas, on Columbus Day, October 14, 1912, “around 30,000 people assembled for the “God and Country” parade. A celebration of American patriotism and antiradicalism, the parade had no place for the hated IWW, and any marcher sporting an IWW button or banner was to be arrested. No manifestation of ethnic loyalty other than American was tolerated, a reflection of the Anglo-Saxon and Irish hostility to “foreigners,” which had been evidenced throughout the strike and defense campaign. Below: Scenes from Lawrence's anti-radical anti-IWW flag parade, held Columbus Day 1912. Source: Louise Sandberg's Queen City archive blog. "The display of Italian flags was expressly forbidden, the national origin of Columbus notwithstanding! Most of the marchers were children from public and parochial schools, municipal employees, members of American patriotic societies, Catholic associations, and some representatives of the AFL. Not more than 4,000 mill operatives participated in the parade, according to I.W.W. organizer Bill Haywood, although it is very likely that many more were bystanders who had turned out to observe a holiday parade but did not subscribe to the anti-IWW objectives it was intended to promote. The IWW, meanwhile, had tried hard to dampen popular enthusiasm for the parade by explaining to the workers, the majority of whom were Catholics, that the IWW had never taken a position against religion, and that the issues of religion and patriotism were being exploited by city officials and mill owners in order to destroy the union. But the IWW’s disclaimer did not succeed in rallying support. Only 4,000–5,000, out of an expected 10,000, showed up for the IWW’s counter-celebration at the picnic grounds in Pleasant Valley.” (Source: Pernicone). It figures, Pleasant Valley at the time was home almost exclusively to Italians. Below: God and Country Banner during the anti-IWW march, October 1912. In the end, pro-American, pro-church, pro-establishment sentiments were victorious over radicalism in Lawrence. The acquittal of Ettor and Giovannitti on November 26, 1912 removed a cause for the radicals, and calmed a lot of people down. Momentum was lost and the IWW failed to organize workers into a permanent union in Lawrence. The history of the IWW in Lawrence is covered in my blog post about the 1919 strike, which everyone in Lawrence seems to have forgotten about but which was just as important as the 1912 strike. By that time, however, the IWW had become unpopular for its opposition to World War I.
Also, the more radical Italian leaders, such as the followers of Galleani, scared the bejesus out of most Americans after they launched their terrorism campaign in 1917. Italian activism subsided just as new immigration rules took off, which led both to the deportation of a lot of the Italian radicals and the end of Italian immigration by 1924. Also, the experience of World War I had made many Italians more patriotic and focused on nationalistic issues rather than class issues, at least on the international political stage. Furthermore, the longer Italian immigrants stayed, the more economically successful they generally became. Because of these trends, from the mid-1920s onward, the story of Italians in Greater Lawrence largely became one of making a place for themselves and making the area a better place. Below: Italian-American fraternal organization, Lawrence, Mass. 1925
1 Comment
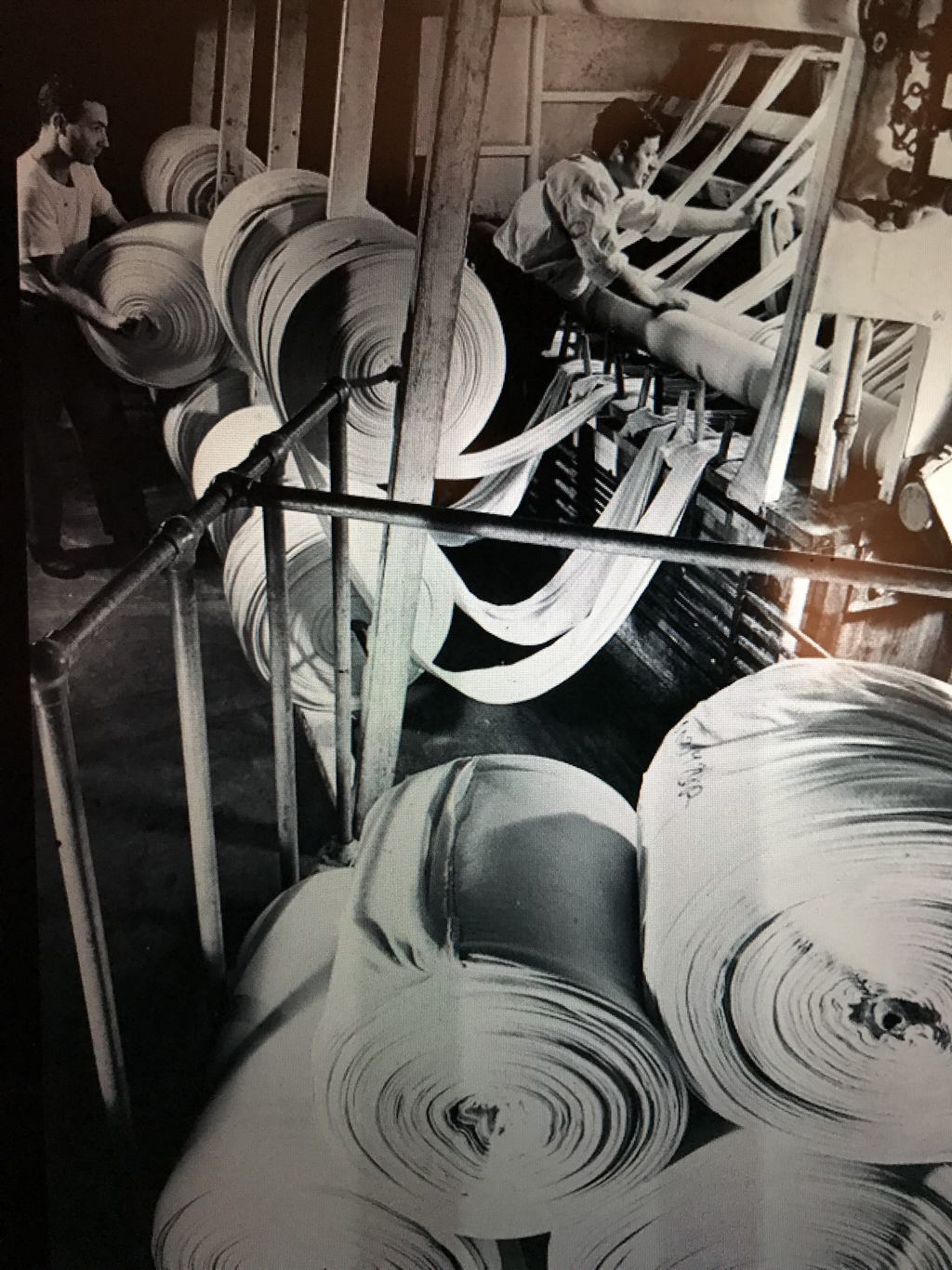
Above: men working in a dyehouse, 1940s Poem 38 Mill Work (a mock poem testimony) by Rich McCarthy, 2011 I was a Lawrence High School student in the 40s. The mills were humming: The Wood Mill, the Ayer Mill, the Arlington, the Pacific. Most every kid had a parent or relative working in a mill. My grandfather had been a weaver here Since he left Vermont at age nineteen (When his father died and the barn burned down.) [My note: the death of his father after a balloon accident is covered in another blog post.] In High School The worst the future could hold for us Was to end up in a mill after graduation We joked about becoming a mill rat. . . no way. My poor dad was a mill rat... in the dye house. And what did I do after I graduated. I took a job. Where? In a dye house. Like dad, I became a “jig” operator It wasn’t bad work; Except for the fumes: The hydrochloric acid, the ammonia, and the formaldrahyde fumes... Whew, sometimes it was overwhelming. I met some interesting people, Like the guy who never wore a shirt And had blue birds tattooed on his chest, One on each breast. Flying towards each other. I only lasted for two months. It wasn’t for me, a kid. I didn’t have to support a family. I left for a job with a magazine distributor. I was out of the mill. It was clean work: Putting up orders for drug stores. But the pay, 65 cents an hour, Stunk So what did I do? I went back to the mill. (The American Woolen Company) One buck an hour? I couldn’t believe it With benefits to boot! A Union shop, the CIO. So there I was, A back-boy Working the second shift, (two to ten), In the mule spinning room. The temperature was hot And humid. . . 90 degrees plus Humidifiers keeping it moist So the ends would not fall. The sweat poured over our brows We all wore head bands To keep it out of the eyes It was so hot we wore pants cut off at the knee, That’s all, no shirt, bare backed And old shoes with no socks It was a nice place to be in a winter storm, tropical. Cockroaches abounded. I stuck it out for about a year. The mills were shutting down, Moving south Where cheaper labor could be found, Or so we heard. So I got “laid off". .. permanently. Lawrence fell into hard times. The textile industry, as Lawrence knew it, Collapsed. But the experience taught me About organized labor, unions. I had got a decent wage. Because the job was so dirty, We were allowed a shower On company time at shift’s end. Because of the union, When we cleaned rollers, The machinery was disengaged. (Back-boys had been killed in prior years, Crushed to death when switches Were accidentally pulled.) Funny, as I think of it, I never heard of the strike of 1912 Not from my working stiff relatives, not in school. So I’m glad this is not the case today In Lawrence. And that we now celebrate The gutsy spontaneous reaction Of exploited immigrants Who made a better future for mill workers... All workers. And I might say, for me personally, A kid back in 1949. Below: The Wood Mill and the Ayer Mill at night, south bank of the Merrimack River, Lawrence, Mass., 1940s
|
|




























 RSS Feed
RSS Feed